Ankle Sprains and Instability
What are the ligaments of the ankle
The ankle joint is a hinge between the leg and the foot. The bones of the leg (tibia and fibula) further stability is provided by the muscles and tendons of the ankle.
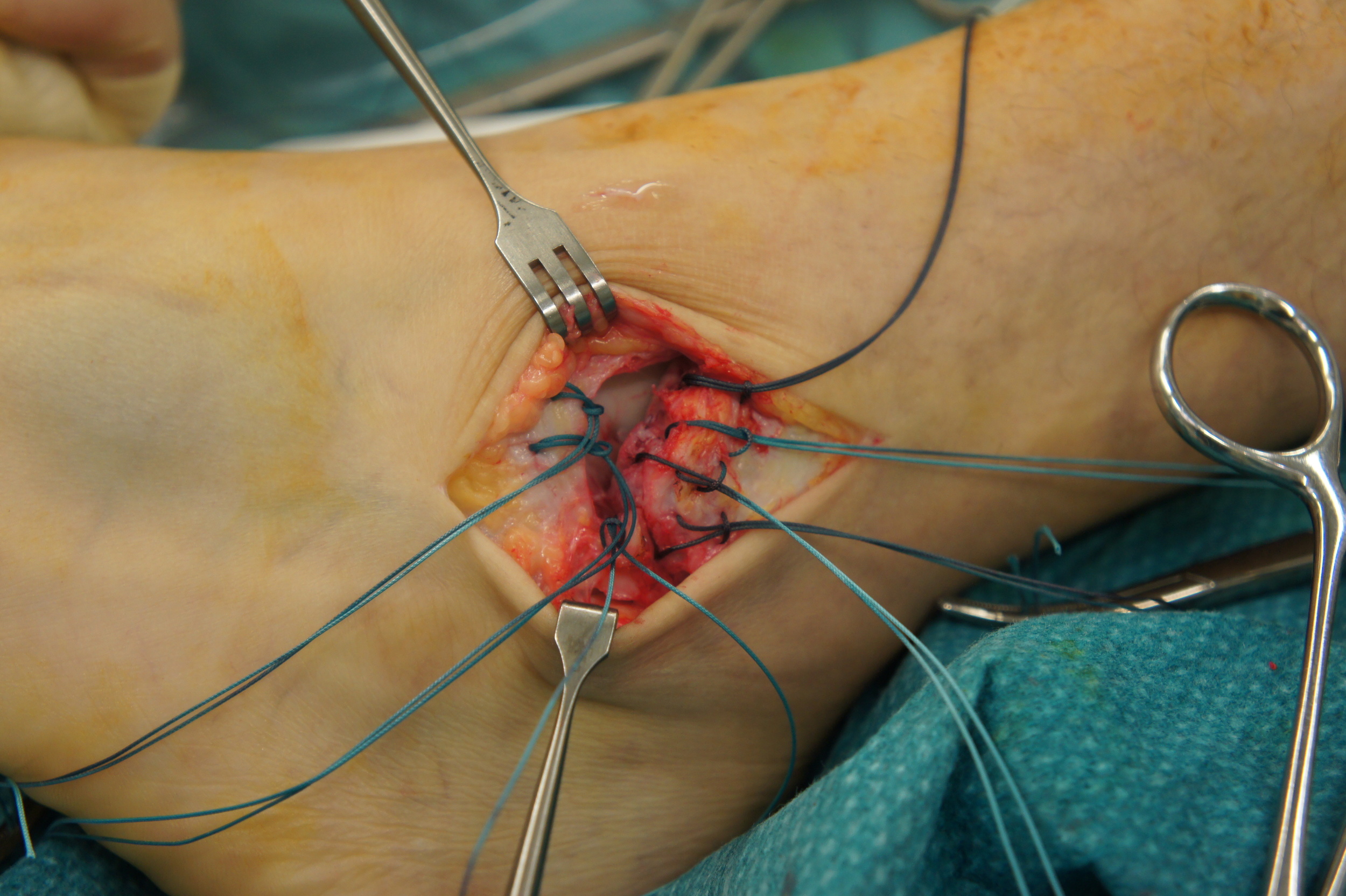
The lateral ligaments are the most frequently injured ligaments. There are three main ligaments that stabilize the outside of the ankle which are demonstrated in the diagram.,. The ATFL (anterior talo-fibular ligament) is the most commonly injured followed by the CFL(calcaneofibular ligament). There is one broad ligament on the inside of the ankle called the deltoid ligament this may be injured in severe ankle sprains and in ankle fractures. There is also a ligament complex securing the tibia and fibula together called the syndesmosis this may be injured during severe sprains (or fractures) sometimes we refer to this as a ‘high ankle sprain’.
How does a sprain occur?
sprains usually occur as a result of an inversion injury where the foot turns inwards, the exact position of the foot and the force involved determine which ligaments are injured and what proportion of each are torn. Ankle sprains present with variable degrees of pain and swelling, severe sprains can make it too painful for you to put weight through the foot.
As the ligaments are torn during a sprain the ankle bone (talus) becomes briefly displaced from the joint and the surface may be damaged, the injury to the joint surface is called an osteochondral injury LINK OSTEOCHONDRAL LESIONS.
How should my sprained ankle be treated?
The majority of simple sprains recover fully within a few days without more treatment than RICE - Rest, Ice, Compression and Elevation. (Do not place ice directly on the skin but wrap crushed ice or a bag of peas within a towel and then place on the swollen area for 15 minutes 4 times a day). you have severe swelling, an inability to weight bear o
n the foot or deformity you should seek urgent medical advice, an X-ray may be required to exclude a fracture.
Even following rupture of one or more of the lateral ligaments the majority of patients return to active sports without the need for surgery.
Early functional rehabilitation with the help of a physiotherapist can help maintain the flexibility, strength, co-ordination (proprioception) and stability of the ankle.
What happens if my ankle sprain doesn’t settle?
proportion of ankle sprains fail to settle and continue to cause pain, stiffness or giving way (instability). Those sprains that are not settling by 3 months, despite proper rehabilitation are called ‘chronic ankle sprains’
Chronic ankle sprains will need further investigation, to exclude scar tissue, localized damage to the joint surface or laxity of the ligaments that might respond to surgical treatment. Injury to joint surface or excessive scar tissue may benefit from an arthroscopy
If the ankle continues to give way, even after intensive physiotherapy, (click here for link to ankle instability) it might be necessary to repair or reconstruct the ligaments.
Be sociable..share!